Introduction
to C Language Beginner’s Guide
In
this tutorial article of introduction to C Language Beginner’s guide, we will
discuss in detail basics and introduction to C Language. We will cover the
introduction to C Language in soft and simple manner for our learners which are
beginners in C Language and had just entered in the C Language learning.
What is C Language
C Language is a high level programming language used for the communication of
the human with computer. And we have to learn C language for the better
understanding of other programming languages especially object oriented
programming like C ++.
History of C
Language
C language the
procedural programming language was first used by Dennis Ritche, an American programmer in 1972, at Americans
Telephone and Telegraphs (AT&T’s), Bell laboratories.
Importance
of C Language
- C language is the most
important language and it is in fact, the first advanced programming language
for general purposes. Following are some primary importance of C Language.
- Ø C language
is a small language, so it is easily understandable by operating system, where
as other languages like C++,C# and Java are complex and big and operating
system feels the difficulties while understanding them.
- Ø Secondly
these programming languages like C++,C# and Java are object oriented languages
and are difficult to learn from start to end without having any grip of C
language.
- Ø Major parts
of all the operating systems like Windows, Linux, Unix are written in C
language.
- Ø Gaming
platforms are also developed using the C Language.
Constants
Variables and Keywords of C Language
To
learn programming language like C is just same as learning the ordinary
language like English. If you want to learn English language you will probably
start with alphabets, then convert them in the words, transform the words in
sentences and then structured the sentences to build a paragraph.
Same
practice is here in C language, you have to first learn the alphabets of C
language which are
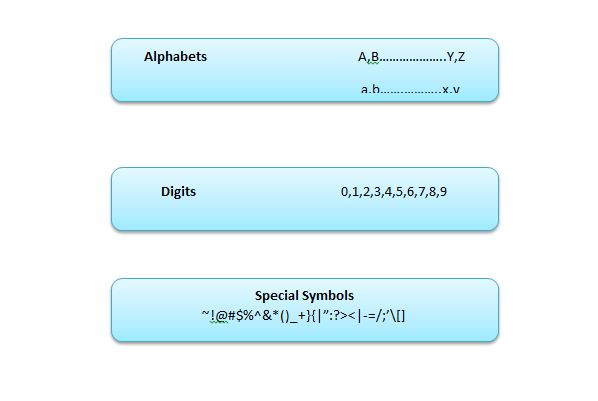
Alphabets,
Digits and Special Symbols
You
will then combine these alphabets, digits and special symbols to form the words
of C language which are
Constants,
Variables and Keywords
These
words must be joined in some logical order to gain the C language sentence
which is
Instructions/Statements
Finally you have to convert these instructions/statements to programs.
Now
we are going to explore the each component of programming language in detail.
Alphabets,
Digits and Special Symbols
We
have all the alphabets capitalized or upper case and lower case or small
letters.
In
Digits, all the digits form 0 to 10 are included.
In
Special symbols, all the symbols such as !,@,#,$ e.t.c are included.
Constants
The
data stored in a variable or memory location is called as constant. In general,
the value which doesn’t change is constant. In programming the data or value
stored in variables or memory locations computer is called as constant.
One
and the only thing to be noted about constant is that constant always stores in
the variables.
Types of
Constants in C language
Basically
in C language we deal with the two types of constants.
Primary
Constant
includes the integer, real and character constants
Secondary Constant includes
the array, pointers, structure, enum etc.
Rules for Integer Constant
- 1. At least one
digit is necessary.
- 2. There is no
decimal point between digits.
- 3. Comma or
blanks around digits is not allowed.
- 4. It may be
positive or negative.
- 5. The range of
integer constant is between -2147483648 to +2147483647.
- 6. Default sign
will be positive.
- For example: +99, -34, -2, +34, 3 are all integer constants.
Rules
for Real Constant
- 1. Must have at
least one digit.
- 2. There must
be decimal point between digits.
- 3. Dash or
comma is prohibited.
- 4. Value may be
positive or negative, whereas default sign is positive.
- For example: +9.9, -3.4, -2.0, +34.0, 3.0 are all real constants.
Exponential Case
Exponential form is usually used in real constants, when either the
value is too large
or too
small, but exponential form never restricts us to form real constants.
The part
before E or e is called as mantissa and after part is exponent.
For Example:
0.0014 can be written as 1.4*10-3 in normal form and 1.4e-3 in exponential form.
Rules
for Exponential Case
1. The mantissa
and exponent are separated by E or e.
2. Mantissa
must be positive or negative, default sign is positive.
3. Exponential
must have at least one digit.
4. Exponent may
be positive or negative, default sign will be positive.
5. Exponential
form must be in between -3.4e38 to 3.4e38 .
For example:
-2.1e-10, 7.7e16, -9.67e-19, 4.1E are
all exponential case real constants.
Rules
for Character Constant
1. Character
constant may be the single alphabet, single digit, of single special symbol
enclosed with in a single inverted comma.
2. The inverted
comma both have the direction to left.
For example:
‘e’, ‘6’, ‘%’ are all exponential case real constants.
Variables
A
variable is simply that store the constants. The variable can also be defined
as entity which holds multiple values or which whose values changes.
In
programming the name given to the particular memory location that holds some
data or value is called as variable.
A
particular type of variable can hold only particular type of data, As integer
type variable will hold the integer type data. Real type variable will hold the
real type data only and character type variable must hold character type data.
The
rules for constructing particular integer, real or character constant are
different but for creating the integer, real or character variable are same.
Rules
for Variables creation
1.
You can use the alphabets, digits and underscore in combination or
individually up to 31 or 247 characters depending on compilers.
2.
Always start the name of variable with _ or alphabets, digit is
not allowed.
3.
Special symbols except _ are prohibited.
4.
No comma or blank is allowed.
For example:
Pe_ple, in_detail, _23hsd, etc are variables name
Possibilities in Variables names
There are
four possibilities in constructing variable names. You can use any possibility
to name a variable.
1. Only
Alphabets
2. Alphabets
and Underscores
3. Alphabets
and digits
4. Alphabets,
digits and underscore
Keywords in
C Language
Keywords
are predefined words for the library of compiler or in broader sense computer
whose meaning is already known to the computer.
There
are too many keywords in different object oriented programming languages but C
Language has only 32 keywords. These are
We
can’t use the keywords as variable names because if we do so it is to assign
the new value to keywords which results in error. So it is safe to use the
meaningful names of variables instead of keywords.
Variables
Declaration in C Language
Assigning
data type to a variable is called as the variable declaration. The point raised
was that rules for creating the variable name for all the primary and secondary
data types are same, so how C compiler differentiate between such variables
names. That’s why the assigning of data type in the declaration of variable is
mandatory so compiler can distinguish the variable name from its data type.
For example: int age; float temp,
char name etc.
Variables
Initialization in C Language
Assigning
the value to a variable is called as variable initialization.
A
variable can be initialized at the same time when it is declared. As
int
age=16;
Or,
A variable can be initialized in separate statement after the declaration. As
int
marks;
marks=300;
Comments in
C Language
Like
all the other programming languages C language also has the facility of
comments in code. These comments are just used to explain the purpose of
program or the purpose of particular statement.
The
text inside the comments is unknown to compiler and hence compiler will not
execute the code in comments and simply ignore this text.
Types of
comments
There
are two types of comments in the C Language.
Single Line
Comment
Single
line comment uses the // in start of line and then comment is written after
these slashes in single line. As
//This
is a single line comment.
Multi Line
Comment
Single
line comment uses the /* in start of comment and */ at the end of comment,
either comment is of one line or it spread over the multiple lines. As
/*Hello!.*/
/*Hello!.
This
is a multi line comment */
OK with this
knowledge in hand we can directly write the program in C language but we will
not do so, we will first understand the basic structure of program in C
Language.
Learn Basic Structure of Program in C language
Thanks for visiting this site keep visiting to learn.






Post a Comment
Feel Free to Comment Us